
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Fasteners are mechanical basic parts and are in great demand. Usually bolts, screws, rivets, etc. are used to ensure safety or generally do not consider the adverse effects of temperature or other dangerous conditions. Commonly used materials are carbon steel, low alloy steel and non-ferrous metals. However, in certain occasions, fastener materials need to meet severe corrosion or high strength conditions, and many stainless steel and ultra-high strength stainless steels have emerged.
This article briefly describes the fine stainless steel used in fastener production. Most stainless steel materials can be made into steel wire or rods for fastener production, including austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel, and precipitation hardened stainless steel.
Material selection principle
The choice of stainless steel materials is mainly considered from the following five aspects.
1. Requirements for the mechanical properties of fastener materials, especially strength;
2. Requirements for the corrosion resistance of materials under working conditions;
3. The requirements of the working temperature on the heat resistance (high temperature strength and oxidation resistance) of the material;
4. Requirements for material processing performance in terms of production process;
5, other aspects, such as weight, price, procurement factors must be considered.
After comprehensive and comprehensive consideration of these five aspects, the final selection of the grades, varieties, specifications, material standards of austenitic stainless steel
The commonly used grades are the four grades of 302, 303, 304, and 305, which are the so-called "18-8" austenitic stainless steel grades. Both corrosion resistance and mechanical properties are similar. The starting point for the selection is the production process of the fasteners, which in turn depends on the size and shape of the fasteners, and also on the quantity produced.
Type 302 is used for machined screws and self-tapping bolts.
Model 303 In order to improve the cutting performance, a small amount of sulfur is added to the Type 303 stainless steel for the processing of nuts with bar stock.
Type 304 is suitable for use in the processing of fasteners using the enthalpy process, such as longer gauge bolts, large diameter bolts, which may exceed the range of the cold heading process.
Type 305 is suitable for use in the processing of fasteners using the cold heading process, such as cold formed nuts, hex bolts.
Types 309 and 310, which have higher Cr content and Ni content than 18-8 stainless steel, are suitable for fasteners working at high temperatures.
Types 316 and 317, both of which contain the alloying element Mo, are therefore higher in strength and corrosion resistance than 18-8 stainless steel.
Types 321 and 347, Type 321 contains a relatively stable alloying element Ti, and Type 347 contains Nb, which improves the intergranular corrosion resistance of the material. Suitable for fasteners that do not anneal after welding or service at 420 to 1013 °C.
Ferritic stainless steel
Type 430 ordinary chrome steel, its corrosion resistance and heat resistance are better than 410 type, it is magnetic, but it can not be heat-treated and strengthened. It is suitable for stainless steel with high strength and resistance to corrosion and heat resistance. firmware.
Martensitic stainless steel
Types 410 and 416 can be heat-treated and reinforced with a hardness of 35 to 45 HRC. They have good machinability and are used for general purpose heat and corrosion resistant fasteners. Type 416 is slightly high in sulfur and is a free-cutting stainless steel.
Type 420, sulfur content? R0.15%, improved mechanical properties, heat treatment strengthening, maximum hardness value 53 ~ 58HRC, for fasteners requiring higher strength.
Precipitation hardening stainless steel
17-4PH, PH15-7Mo, they can be used with higher strength than the usual 18-8 stainless steel and are therefore used in high strength, corrosion resistant stainless steel fasteners.
A-286, a non-standard stainless steel, has higher corrosion resistance than the commonly used 18-8 stainless steel and good mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. Used as a high-strength, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant fastener, it can be used up to 650-700 °C.
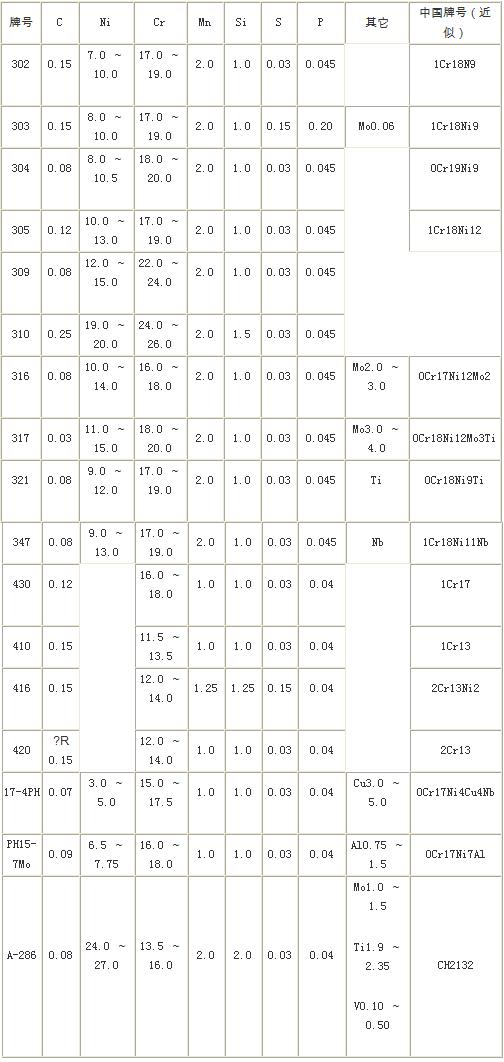
Table fasteners with stainless steel
October 19, 2024
July 03, 2024
November 25, 2023
Contactar proveedor
October 19, 2024
July 03, 2024
November 25, 2023

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.